Understanding Co-occurring Disorders: A Comprehensive Guide
Welcome to our in-depth exploration of co-occurring disorders, a complex and often misunderstood topic in the realm of mental health. In this article, we will delve into the nuances of co-occurring disorders, also known as dual diagnosis or comorbidity, providing you with a thorough understanding of this phenomenon. By the end of this read, you will have gained valuable insights into the intersection of mental health and substance abuse, the challenges individuals face when dealing with co-occurring disorders, and the most effective strategies for diagnosis and treatment.
The Intersection of Mental Health and Substance Abuse

Co-occurring disorders refer to the presence of both a mental health disorder and a substance use disorder in an individual. These disorders often coexist and interact with one another, complicating the diagnosis and treatment process. The relationship between mental health and substance abuse is complex, with each condition influencing and exacerbating the other. For example, individuals with a mental health disorder may turn to substances as a way to self-medicate or cope with their symptoms, leading to substance abuse. Conversely, substance abuse can trigger or worsen underlying mental health issues, creating a vicious cycle of co-occurring disorders.
Research has shown that individuals with co-occurring disorders have higher rates of hospitalization, incarceration, homelessness, and overall poorer outcomes compared to those with a single diagnosis. The coexistence of mental health and substance use disorders presents unique challenges for both individuals and healthcare providers, requiring a comprehensive and integrated approach to treatment.
Diagnosis and Assessment of Co-occurring Disorders
Diagnosing co-occurring disorders can be challenging due to the overlapping symptoms and complexities involved. Healthcare providers must conduct a thorough assessment to identify both the mental health disorder and the substance use disorder accurately. This process often involves a combination of clinical interviews, standardized questionnaires, and laboratory tests to assess the individual’s mental health status, substance use patterns, and overall functioning.
It is essential for healthcare providers to adopt a holistic approach when assessing co-occurring disorders, considering the interconnected nature of mental health and substance abuse. By understanding the underlying factors contributing to the co-occurrence of these disorders, clinicians can develop more targeted and effective treatment plans tailored to the individual’s specific needs.
Treatment Approaches for Co-occurring Disorders

The most effective treatment for co-occurring disorders is an integrated approach that addresses both the mental health and substance abuse components simultaneously. This integrated treatment model emphasizes the importance of coordination between mental health professionals and addiction specialists to provide comprehensive care for individuals with co-occurring disorders.
Some common treatment approaches for co-occurring disorders include:
Dual Diagnosis Treatment Programs:
These specialized programs are designed to address the unique needs of individuals with co-occurring disorders. They typically combine individual therapy, group therapy, medication management, and behavioral interventions to help individuals achieve and maintain recovery.
Medication Management:
Medications may be prescribed to manage symptoms of mental health disorders, such as depression, anxiety, or psychosis, while also addressing substance withdrawal and cravings. It is essential for healthcare providers to carefully monitor the individual’s response to medications and make adjustments as needed.
Psychotherapy:
Various forms of therapy, such as cognitive-behavioral therapy (CBT), dialectical behavior therapy (DBT), and motivational interviewing, can be beneficial in treating co-occurring disorders. These therapeutic approaches help individuals develop coping skills, improve emotional regulation, and address maladaptive behaviors associated with both mental health and substance use disorders.
Challenges in Treating Co-occurring Disorders
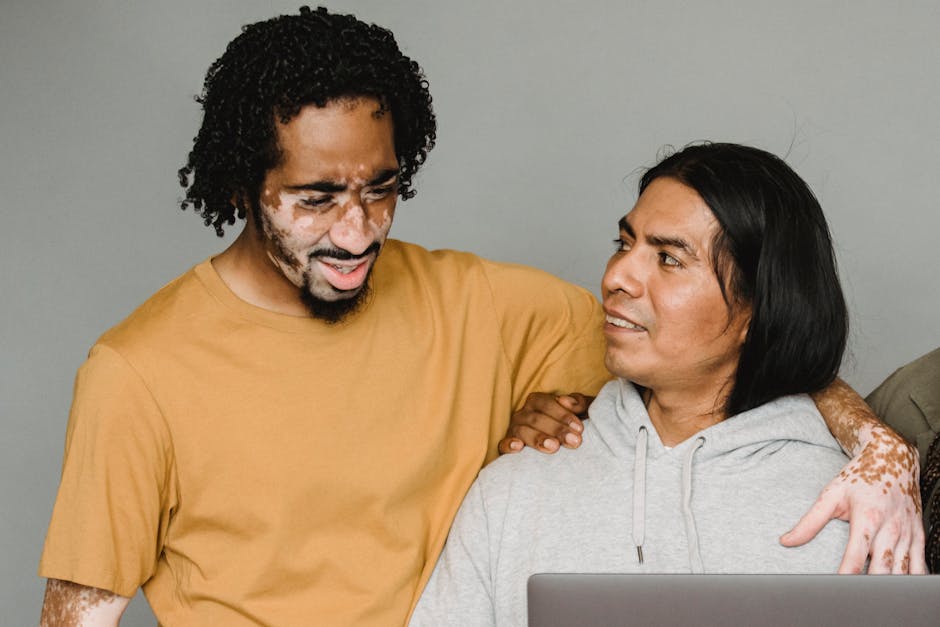

While integrated treatment programs have shown promising outcomes for individuals with co-occurring disorders, there are several challenges that healthcare providers may encounter along the way. Some of the common challenges include:
Stigma and Discrimination:
Individuals with co-occurring disorders may face stigma and discrimination from society, healthcare providers, and even within their own families. This can hinder their willingness to seek help and adhere to treatment, leading to poorer outcomes.
Complexity of Diagnosis:
Diagnosing and assessing co-occurring disorders can be complex and time-consuming, requiring specialized training and expertise. Healthcare providers must be able to differentiate between symptoms of mental health disorders and substance use disorders to provide accurate and effective treatment.
Lack of Access to Integrated Care:
Despite the growing recognition of the need for integrated treatment for co-occurring disorders, many individuals still face barriers to accessing comprehensive care. Limited resources, lack of trained professionals, and fragmented healthcare systems can make it challenging for individuals to receive the necessary support.
Common Misconceptions about Co-occurring Disorders
There are several misconceptions and myths surrounding co-occurring disorders that can contribute to misunderstandings and stigma. It is essential to debunk these misconceptions to promote a better understanding of the complexities involved in treating co-occurring disorders.
Myth: Co-occurring disorders are rare.
Fact: Co-occurring disorders are more common than people realize, with a significant portion of individuals seeking treatment for mental health issues also experiencing substance use problems.
Myth: You can’t treat both disorders at the same time.
Fact: Integrated treatment approaches have been proven to be effective in addressing both mental health and substance use disorders simultaneously, leading to better outcomes for individuals with co-occurring disorders.
Myth: People with co-occurring disorders are hopeless cases.
Fact: With the right support and treatment, individuals with co-occurring disorders can achieve and maintain recovery, leading fulfilling and productive lives.
Conclusion
To wrap things up, understanding co-occurring disorders is crucial in providing effective care and support for individuals facing the complex interplay of mental health and substance abuse. By adopting an integrated treatment approach, addressing stigma and discrimination, and promoting access to comprehensive care, we can make a significant impact in the lives of those with co-occurring disorders. Let’s continue to educate ourselves and others about the importance of recognizing and addressing co-occurring disorders to ensure that everyone has the opportunity to live a healthy and fulfilling life.
Thank you for joining us on this journey to explore the intricacies of co-occurring disorders. If you have any questions or would like to share your thoughts and experiences, please feel free to reach out. Together, we can create a more inclusive and supportive environment for individuals with co-occurring disorders.